Disclaimer, I am not a lawyer, This is not legal advice. Consult a lawyer (I just play one on TV) if you don’t understand this material or the references herein.
Transportation Law
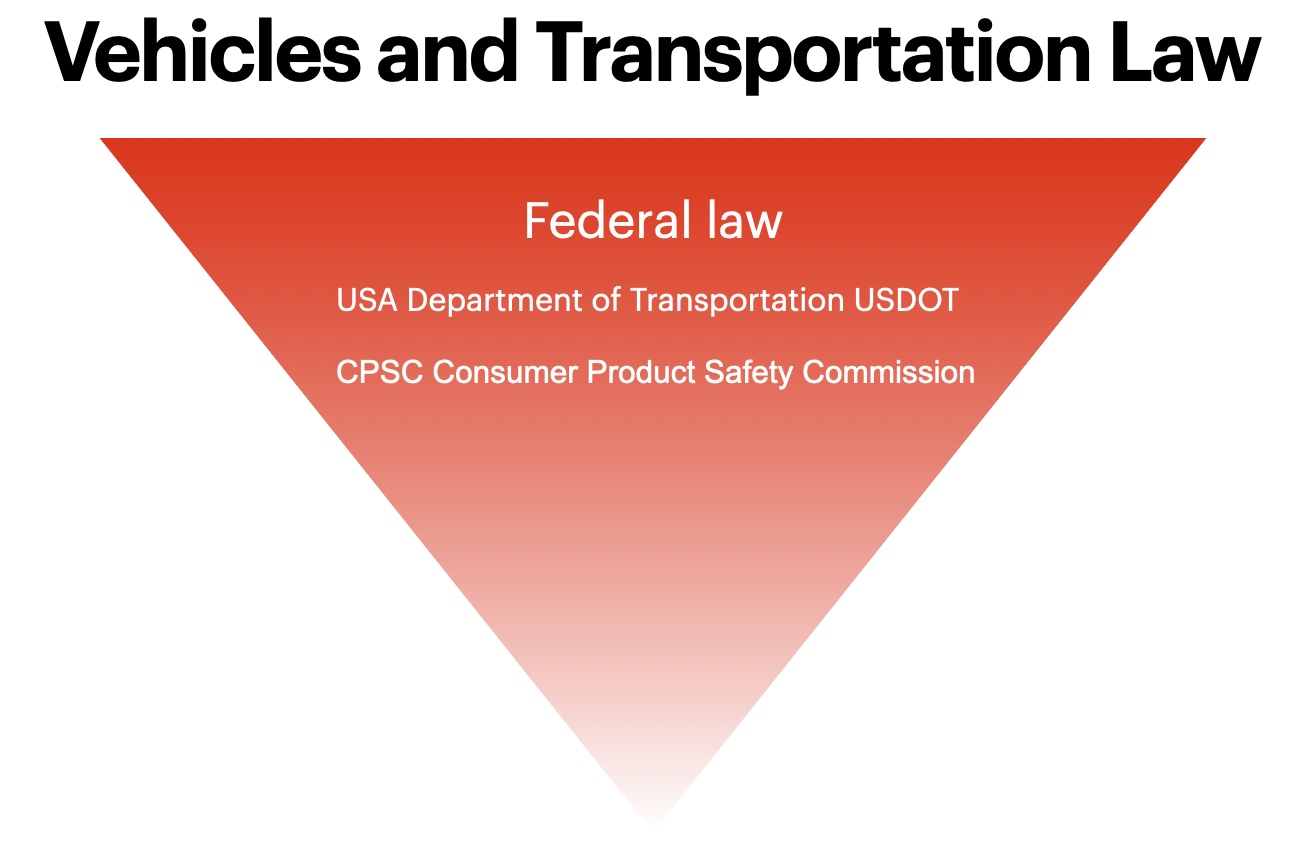
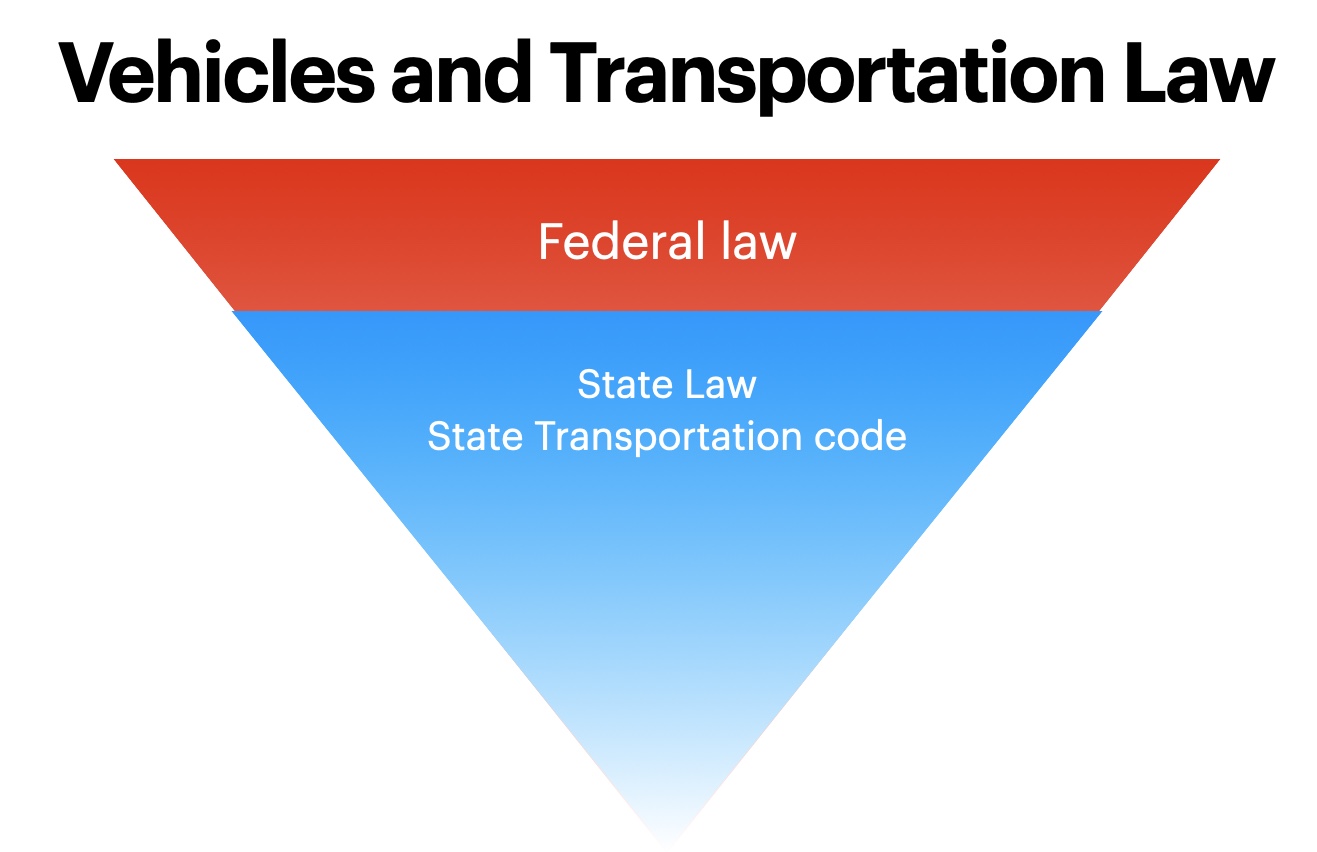
There are layers and layers of law in the USA. Visually, you can picture them as an upside-down wedding cake, with federal law being the large part at the top and some municipalities code at the small point at the bottom.
An Overview of Transportation Law
Transportation law is a broad legal field encompassing federal and state transportation statutes. These laws involve transportation infrastructure and all forms of road, railway, water and air transport.
Transportation law may apply to:
- Surface vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, buses and bicycles
- Aircraft, including planes, helicopters and drones
- Watercraft, including boats, ships and freighters
- Railroad systems, including trains and subways
- Infrastructure, including roads, bridges, railways, airports, shipping ports and trails
State transportation codes
State law (called codes) specifies the definitions of and operation of vehicles (including bicycles) on their streets. Typically they have a section that defines what a vehicle is, how and where it can be operated and any restrictions to that operation, education, insurance, inspection, license, and registration requirements in the state. In the case of bicycles, most (but not all) define bicycles as vehicles and have the rights and responsibility the same any other vehicle being operated on the road.
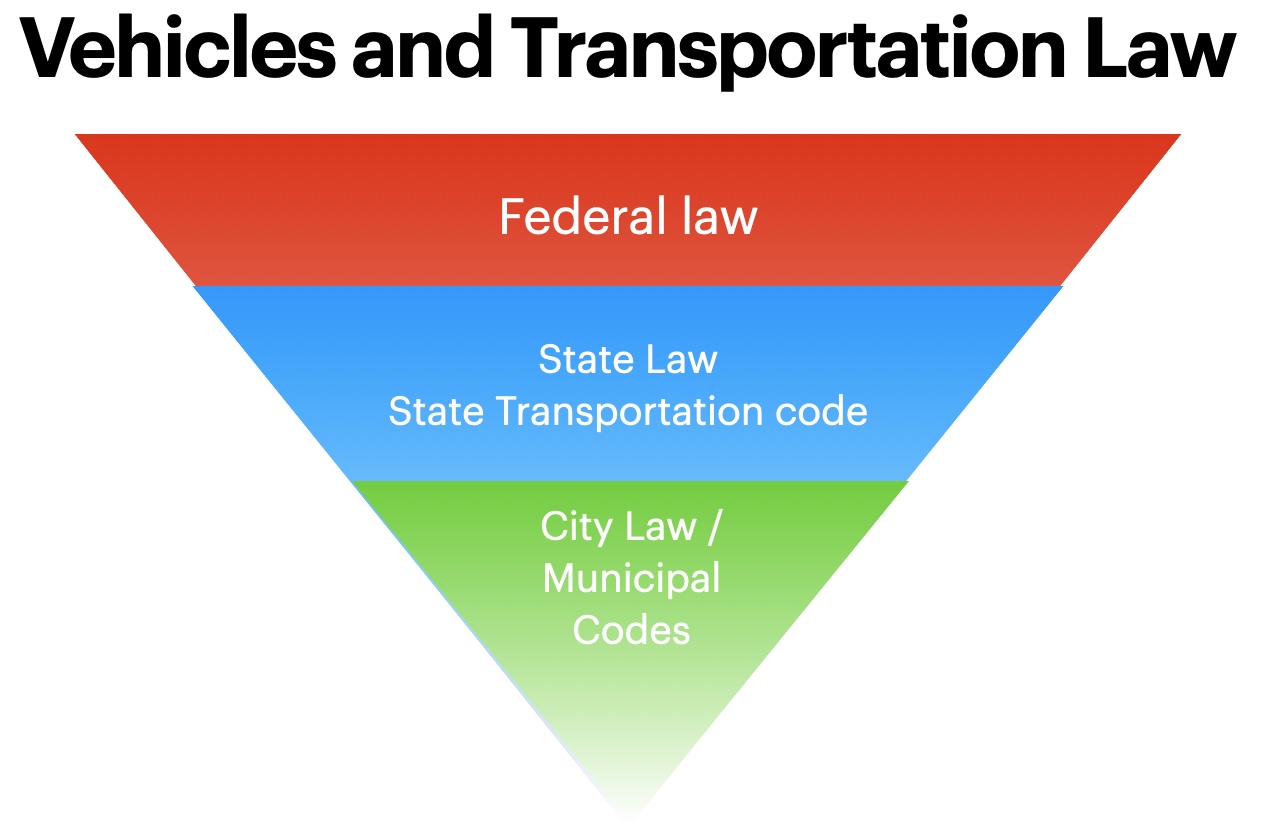
Cities and Municipalities
cities may have their own governance for operations on streets and facilities which they own or maintain. This gets a bit tricky as “state highway” would be governed by the state whereas a “city street” would be governed by the city itself. When a highway goes through city maintenance and if the segment of the road was deeded over to the city from the state can control jurisdictions and rules. In some states, cities have passed “passing rules” that are meant to keep cyclists and other vulnerable road users safe when the states do not have such codes. Once you leave the city through the rules change to the next city or back to the state. This may include trail use, sidewalk use or even if cyclists can use part of a city street.
Federal Transportation Law
Congress is authorized to regulate interstate commerce under the U.S. Constitution. This means that travel between the states is subject to several federal laws and regulations.
The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) is the umbrella agency for all federal transportation policies and regulations. The DOT’s stated goals are to keep the traveling public safe, increase national mobility, and support the national economy through the transportation system. The DOT oversees several agencies that administer federal statutes for various branches of transportation, including:
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, which is responsible for motor vehicle and highway transportation safety standards and regulations
- The Federal Aviation Administration, which is responsible for airport, air traffic and aircraft regulation
- The Federal Highway Administration, which is responsible for laws pertaining to commercial freight and the maintenance and preservation of interstate highways, tunnels and bridges
- The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration, which is responsible for safety regulation laws for large commercial vehicles
- The Federal Railroad Administration, which is responsible for regulating the safety and development of the U.S. railroad system
- The Federal Transit Administration, which provides financial and technical assistance to local public transportation systems
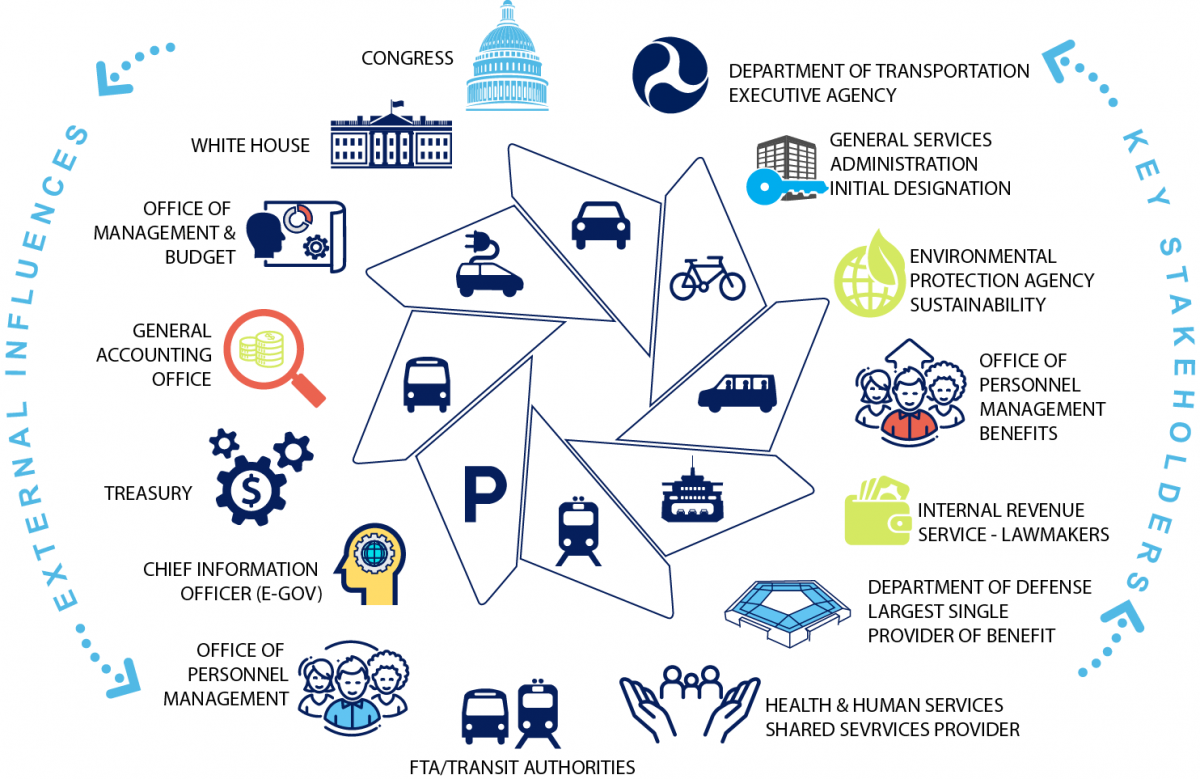

US Department of Transportation (USDOT)
U.S. DOT includes several agencies, or operating administrations, each with a specific focus and authority. These include the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), Federal Transit Administration (FTA), Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), and the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA). Each of these agencies is helping to improve bicycling and pedestrian safety, and each has particular associated roles and responsibilities. U.S. DOT pedestrian and bicycle efforts are coordinated through the U.S. DOT Pedestrian and Bicycle Coordinating Committee, which monitors progress in bicycle and pedestrian safety and use; identifies new cross-modal opportunities and partnerships with outside entities to advance pedestrian and bicycle transportation; and communicates, coordinates, and shares information across Operating Administrations within U.S. DOT on pedestrian and bicycle transportation activities

Pedestrian and Bicycle Information Center
The Pedestrian and Bicycle Information Center (PBIC) is supported by FHWA and NHTSA, and housed within the UNC Highway Safety Research Center. Its mission is to improve the quality of life in communities through the increase of safe walking and bicycling as viable means of transportation and physical activity
National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB)
The U.S. National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent federal agency that provides certain safety guidelines and investigates mass transit accidents, such as plane and train crashes. The agency works on major investigations throughout the U.S. and abroad. The NTSB wants information from board investigations to improve transportation safety. That’s why NTSB findings of an accident (like fault or probable cause) generally cannot be used as evidence in court.


Consumer Product Safety Commission CPSC
Also related to this is the Consumer Product Safety Commission CPSC which has the authority to set and regulate products (such as Bicycles) as consumer items
The United States Consumer Product Safety Commission is an independent agency of the United States government. The CPSC seeks to promote the safety of consumer products by addressing “unreasonable risks” of injury; developing uniform safety standards; and conducting research into product-related illness and injury
- The United States Consumer Product Safety Commission is an independent agency of the United States government. The CPSC seeks to promote the safety of consumer products by addressing “unreasonable risks” of injury; developing uniform safety standards; and conducting research into product-related illness and injury
- The CPSC has the authority to set and regulate products (such as Bicycles) as consumer items.
Want More Information? Watch our videocast here!
Or jump directly to any of the topics
Want to contact us, or anyone else? scroll down for our information and a contact form, email, telephone number etc.

4101 East Park Blvd #138
Plano Texas 75094
+1 214-556-0997